Alpine Soil - Australia
- What role do the Alpine soils play in the water supply of Southeast Australia, and why is their preservation so crucial?
The alpine soils play a crucial part in the flow of water supply in Southeast Australia as they solidify the water sources through irrigation, and maintain the health of the alpine. They are essential for many ecosystems as well.
- What are the primary threats to Alpine soils, and how do these threats impact the environments and water systems?
Visitation and feral animals such as horses, deer and pigs are some of the main threats to Alpine soils, as they are very vulnerable to loss via changes of temperature and disturbance, which impact the environments and water systems surrounding them.
- How was the ground cover in the Australian Alps changed over the years, and what restoration efforts have been key to this improvement?
Hay was spread over sown seed patches to protect the environment and ecosystems from further degradation, and to improve it.
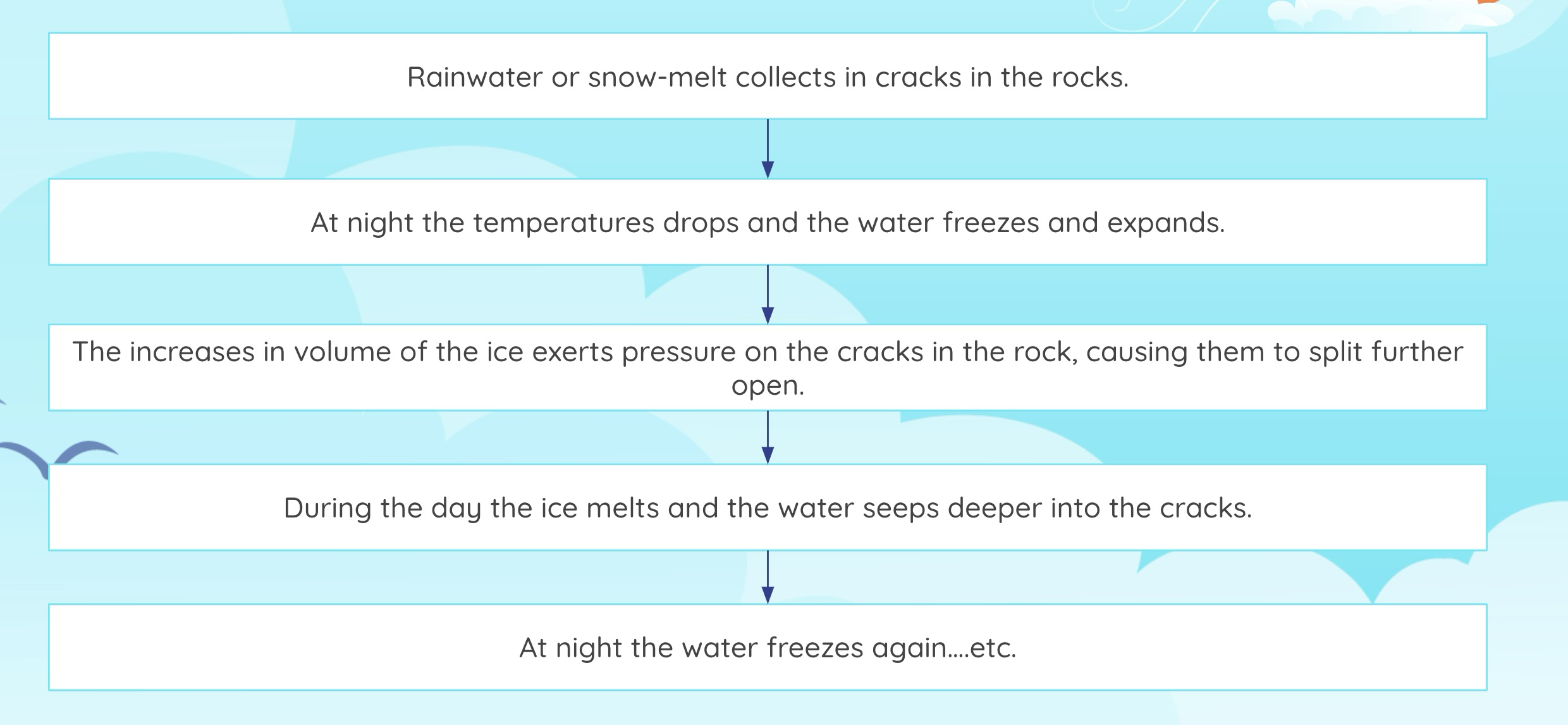
Physical Weathering
Physical weathering is caused by the effects of changing temperature on rocks, causing the rock to break apart. The process is sometimes assisted by water.
There are two main types of physical weathering:
- Freeze-thaw occurs when water continually seeps into cracks, freezes and expands, eventually breaking the rock apart.
- Exfoliation occurs as cracks develop parallel to the land surface a consequence of the reduction in pressure during uplift and erosion.
Where does it occur: Physical weathering happens especially in places places where there is little soil and few plants grow, such as in mountain regions and hot deserts.
How does it occur: Either through repeated melting and freezing of water (mountains and tundra) or through expansion and contraction of the surface layer of rocks that are baked by the sun (hot deserts).
Freeze/Thaw effect